AWS NAT Gateway: Pricing, Optimization & Cost-Saving Tips
Are you wrestling with the ever-increasing costs of your cloud infrastructure? Understanding the intricacies of AWS NAT Gateway pricing is crucial for optimizing your cloud spend and preventing unexpected bills.
Navigating the complexities of cloud services can often feel like traversing a maze. Hidden costs, fluctuating charges, and the sheer volume of available options can make it challenging to make informed decisions. One area where these complexities often manifest is in network address translation (NAT) services, particularly within the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ecosystem. The AWS NAT Gateway, a managed service facilitating outbound internet access for instances within a private subnet, is a critical component for many cloud deployments. However, its pricing model, if not carefully understood and managed, can lead to significant and often unforeseen expenses.
Let's delve into the world of AWS NAT Gateways, exploring their cost structure, operational considerations, and strategies for effective cost optimization. This analysis is not just for the technically inclined; it's for anyone responsible for cloud spending, seeking to make the most of their AWS resources while maintaining a lean and efficient infrastructure.
- Astrology For Couples Enhance Your Relationship With The Stars
- Stylish Icons Male Celebrities With Fringes
| Aspect | Details |
| Service Overview | A managed service within AWS, enabling instances in private subnets to connect to the internet or other services outside the VPC without exposing their private IP addresses. |
| Primary Use Cases | Providing outbound internet access for software updates, accessing external APIs, or connecting to other services outside the VPC. |
| Key Benefits | Simplified network management, enhanced security, and improved availability compared to self-managed NAT instances. |
| Pricing Model | Primarily based on hourly rates for gateway provisioning and data processing charges. |
| Regional Availability | Available in all AWS regions. The specific pricing varies by region. |
| Cost Optimization Strategies | Careful monitoring of data transfer volumes, selection of appropriate instance types, and consideration of alternatives such as VPC endpoints and private links. |
| Managed vs. Self-Managed | Offers advantages over self-managed NAT instances in terms of scalability, high availability, and reduced management overhead. |
| Monitoring | Monitoring of traffic volume, CPU utilization, and error rates to identify potential bottlenecks and cost inefficiencies. |
| Availability Zone Considerations | NAT Gateways are designed to be highly available within an Availability Zone. Consider placement across multiple AZs for resilience. |
| Integration with Other AWS Services | Seamlessly integrates with other AWS services like EC2, S3, and CloudWatch for monitoring and management. |
The pricing of an AWS NAT Gateway, while seemingly straightforward, has several facets that need close attention. Ignoring these can lead to unpleasant surprises on your monthly bill. Understanding these components is the first step in controlling your costs and ensuring that your cloud infrastructure remains financially sustainable. The cost structure can be broken down into the following key elements:
Hourly Rate: AWS charges a fixed rate for each hour the NAT Gateway is provisioned and available in your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). This charge is incurred regardless of whether the gateway is actively processing any traffic. The hourly rate varies depending on the AWS region where the NAT Gateway is deployed. For instance, a NAT Gateway in the US East (N. Virginia) region might incur a different hourly charge compared to one in the EU (Ireland) region.
Data Processing Charges: In addition to the hourly rate, you are charged for every gigabyte of data processed by the NAT Gateway. This is arguably the most variable cost component, as it directly correlates with the volume of outbound data your instances are transmitting. The data processing charge also varies by region. This means that the same amount of data processed through a NAT Gateway in one region might cost more or less than in another.
- Elegant Wedding Updos For Black Hair Timeless Styles For Your Special Day
- Optimal Choices For Best Cheap Testosterone Booster
Data Transfer Costs: Standard EC2 data transfer charges also apply when data is transferred out to the internet. These charges are in addition to the NAT Gateway data processing charges and can add up significantly, especially for applications that generate a lot of outbound traffic.
Understanding the Components:
- Hourly Rate: The cost for keeping the NAT Gateway running.
- Data Processing: Costs associated with the data the NAT Gateway processes.
- Data Transfer: Charges to get data to the internet.
The costs associated with a NAT Gateway, though simple to outline, can quickly escalate if not monitored and managed efficiently. Several variables affect the final cost, making it essential to understand how these charges accumulate and to actively implement strategies to mitigate expenses.
The interplay of these pricing factors emphasizes the need for strategic planning and consistent monitoring. Simply deploying a NAT Gateway and forgetting about it can be an expensive mistake. A proactive approach to understanding and managing these costs will pay dividends in the long run, ensuring that your cloud infrastructure operates efficiently and remains cost-effective.
One of the primary drivers of NAT Gateway costs is data transfer. This directly affects the processing charges mentioned above. Data transfer charges are incurred when data leaves your VPC and traverses the internet. The volume of data transferred, the destination, and the AWS region all influence these costs. Therefore, it's crucial to monitor data transfer volumes closely and identify any applications or services that are generating excessive outbound traffic. This is an essential step in understanding the true cost of your NAT Gateway usage.
Furthermore, the specific AWS region in which your NAT Gateway resides plays a significant role. As mentioned earlier, both the hourly rate and the data processing charges vary by region. This means that a simple move to a different region might result in a lower or higher overall cost. Careful evaluation of the pricing in different regions is a key consideration for cost optimization. The decision to select a specific region should therefore align with your overall business strategy, data residency requirements, and cost considerations.
The deployment of the NAT Gateway within the architecture of your VPC is another critical cost factor. For instance, centralizing your NAT Gateway using a transit gateway may introduce additional data processing charges related to the transit gateway itself. In contrast, a distributed architecture, where you deploy a NAT Gateway in every VPC, may have different cost implications. Choosing the appropriate architectural design is, therefore, an important element of your overall cost strategy.
The type of traffic that flows through your NAT Gateway also impacts costs. If a large amount of data is being transferred through the NAT Gateway from specific VPCs, maintaining the NAT traffic locally within the VPC could be more cost-effective. Understanding the patterns of your data transfer and the nature of your application's communication requirements is thus essential to make optimal cost-related decisions.
To further compound these cost elements, the choice between a NAT Gateway and a NAT instance impacts your costs. A NAT instance is essentially an EC2 instance configured to perform NAT. Its cost structure includes the EC2 instance costs, data transfer charges, and any associated storage or EBS costs. In contrast, a NAT Gateway is a managed service, and its costs depend on the hourly rate and data processing charges. While NAT instances might initially seem cheaper, NAT Gateways can become more cost-effective at higher data transfer volumes due to their optimized data processing capabilities and built-in scalability. Therefore, the choice between these two depends on your specific workload, data transfer volume, and operational requirements.
Managing your NAT Gateway costs isn't merely about understanding the costs; it's about implementing strategies to optimize them. There are several techniques you can employ to minimize these expenses without compromising the functionality or performance of your cloud environment. These strategies range from architectural considerations to practical operational practices.
One of the most effective strategies is to closely monitor your data transfer volumes. AWS CloudWatch provides detailed metrics on data processed by your NAT Gateways, including bytes processed, and error counts. Regularly analyzing these metrics allows you to identify any applications or services that are generating excessive outbound traffic. If you identify such applications, you can explore alternative solutions, such as optimizing data transfer, using private links, or leveraging VPC endpoints, all of which might potentially reduce your data transfer costs.
Consider architectural changes. When designing your network architecture, carefully assess where the NAT Gateway is placed relative to your resources. For instances that don't require internet access, you could consider placing them in private subnets without a direct route to the internet. This reduces the amount of traffic processed by the NAT Gateway, leading to cost savings.
When designing your applications, prioritize efficient data transfer practices. For example, if you're transferring files to an S3 bucket, consider using a VPC endpoint for S3. VPC endpoints allow you to connect to Amazon S3 without needing an internet gateway or NAT Gateway. This circumvents the data processing and data transfer costs associated with using a NAT Gateway. Furthermore, optimizing the data transfer process itself can significantly reduce costs. Techniques include compressing data before transfer, implementing data caching, and using efficient data transfer protocols.
Another crucial aspect is choosing the right region. As we discussed, the hourly rate and data processing charges vary by AWS region. Comparing the pricing of the NAT Gateway in different regions can inform your decision on where to deploy your infrastructure. If possible, locate your resources closer to the region where your users are, to minimize latency and potentially lower data transfer costs. This decision must be weighed against your existing infrastructure and data residency requirements, but it's a consideration nonetheless.
Additionally, scrutinize your existing traffic patterns to identify opportunities for cost optimization. If your workload involves high amounts of outbound data, explore whether it's possible to keep the traffic within the same Availability Zone (AZ) as the NAT Gateway. Keeping traffic local within an AZ can help reduce data transfer costs, potentially saving money. Evaluate all the components within your VPC, from the EC2 instances to the S3 buckets, and make informed decisions to keep the traffic as local as possible.
Another practical strategy to improve cost management is to tag your NAT Gateways with relevant metadata. This allows you to accurately allocate costs across different projects, teams, or environments. Tagging enables a more granular view of your cloud spending, allowing you to pinpoint where costs are accumulating and which specific services are driving those costs.
Regularly assess the need for NAT Gateways. If some of your resources do not require internet access, then you could consider removing their direct access to the NAT Gateway. This reduces unnecessary data processing charges. If you are using a NAT Gateway in multiple availability zones, ensure you are following AWS best practices to reduce data transfer costs. For instance, you should ensure that the resources needing access to the internet are in the same Availability Zone as the NAT Gateway. Otherwise, you might incur additional data transfer costs between Availability Zones.
Finally, remember that the cloud is constantly evolving. AWS regularly updates its services, including pricing models. Stay informed about any changes to NAT Gateway pricing or new features that might affect your costs. Regularly review your cloud environment and adapt your cost optimization strategies to reflect these changes. The cloud cost optimization process is ongoing; therefore, staying informed is essential for maintaining a cost-effective cloud infrastructure.
Article Recommendations
- Achievements Of Halle Berry A Trailblazing Career In Hollywood
- Secrets Of The Zodiac The Truth About Not All Geminis

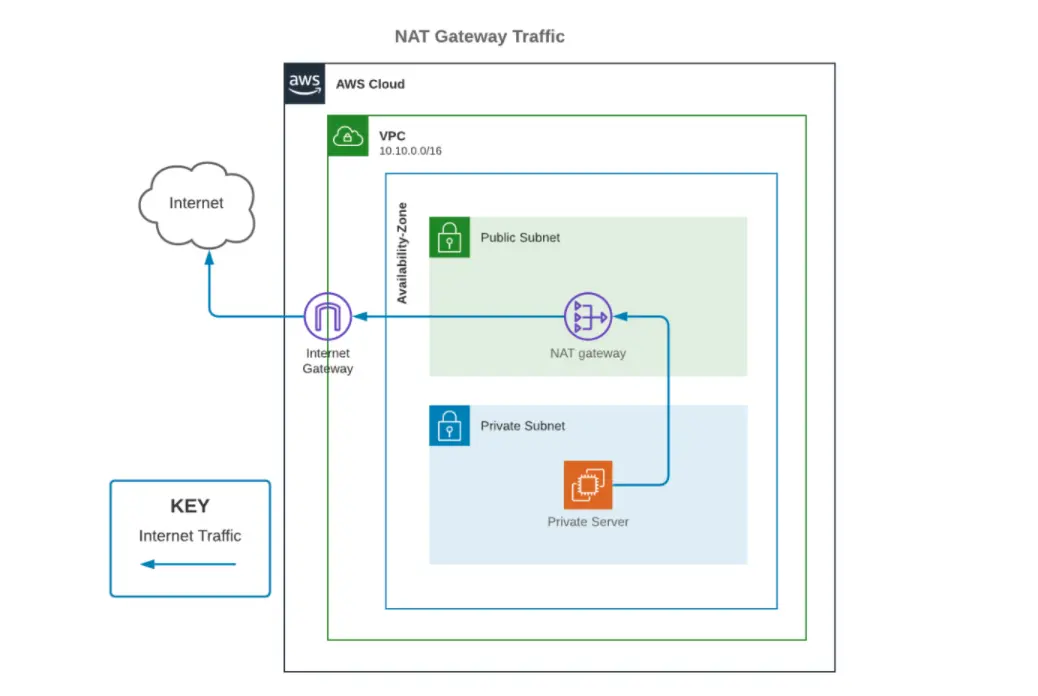
Detail Author:
- Name : Ms. Rosalee Bernhard I
- Username : ddurgan
- Email : kdibbert@wehner.com
- Birthdate : 1985-05-24
- Address : 904 Collins Plains Suite 150 East Syblehaven, SC 59566
- Phone : +1.480.667.7697
- Company : Kessler LLC
- Job : Bartender Helper
- Bio : Consequatur occaecati quos quod sed qui harum ipsa. Aperiam quia et nostrum omnis repellendus debitis ipsa aut. Et provident est vitae in. Aliquam quos quia ut et.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/lloyd.ferry
- username : lloyd.ferry
- bio : Ut incidunt in odio voluptate. Excepturi pariatur hic dignissimos.
- followers : 2300
- following : 1015
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/lloyd_real
- username : lloyd_real
- bio : Numquam eaque porro reiciendis nihil. Sint sequi autem sapiente beatae. Sit aliquam ipsum est totam vitae.
- followers : 6852
- following : 1210