AWS NAT Gateway Cost: Avoid Overspending & Optimize!
Ever wondered how a seemingly simple network component can lead to a cascade of costs? The seemingly straightforward act of provisioning a NAT gateway can quickly become a significant line item in your AWS bill, often leaving users puzzled by unexpected charges.
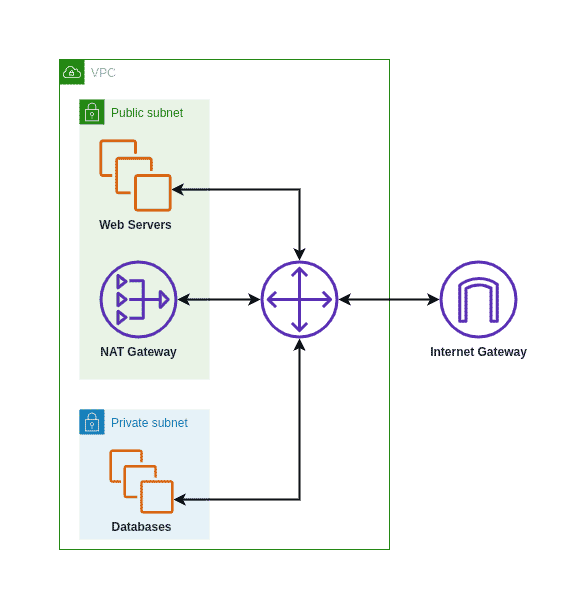
When you provision a NAT gateway in Amazon Web Services (AWS), you're essentially paying for two primary things: the time it's available and the amount of data it processes. AWS charges for each hour your NAT gateway is up and running, and for every gigabyte of data that flows through it. This is not a trivial consideration; it's a fundamental aspect of understanding and managing your cloud expenses effectively.
The costs associated with NAT gateways, however, are not always transparent. Understanding the components that contribute to the overall cost is key to efficient cloud resource management. The two main factors are the hourly usage, which is a fixed cost for simply having the gateway available, and data processing charges, which vary depending on the volume of traffic. Furthermore, there are data transfer costs associated with moving data between your EC2 instances and the internet. These additional charges can quickly escalate the overall expenses if not closely monitored and managed effectively.
- Mastering The Art Essential Tips For Tattoo Success
- Transforming Your Look A Complete Guide To Layers In Wavy Hair
Lets delve deeper into the cost structure of NAT Gateways and explore how you can optimize your AWS spending without compromising performance or security.
The financial structure behind NAT gateways can appear simple at first glance. However, the cumulative effects of these costs can be substantial. You're charged for each hour the NAT gateway is provisioned, regardless of whether it's actively used or idle. The rate, while seemingly small on an hourly basis, accumulates over time. Then there's the data processing cost. This is applied to every gigabyte of data processed by the gateway, irrespective of whether the traffic's origin or intended recipient. Then, data transfer costs are incurred when moving data between your EC2 instances and the internet, adding another layer to the total expense.
The nature of NAT gateways, unlike EC2 instances, do not offer the flexibility of reserved instances or spot pricing options, limiting your ability to reduce costs through these common savings strategies. The lack of these options makes it even more critical to optimize the usage and configuration of your NAT gateways to keep expenses under control.
- July Zodiac Cancer Amp Leo Traits Compatibility And More
- Pin Up Hair Styles Timeless Elegance And Modern Flair
Consider a scenario where you set up a NAT gateway to provide internet access to your private subnet resources. The hourly charge for the NAT gateway begins immediately. Now, imagine a scenario where your EC2 instances are regularly communicating with an external service, say, an API for weather data. As your instances send requests and receive responses through the NAT gateway, data processing charges are accumulated for every gigabyte of data, both incoming and outgoing. If the data transfer is substantial, particularly across regions or to the internet, the associated costs can quickly add up, making this simple setup significantly more expensive over time. Proper planning, efficient usage, and traffic optimization become essential.
Pricing starts at $0.045 per NAT gateway hour plus data processing and data transfer charges. The data processing costs are based on the amount of data that flows through the NAT gateway. For example, if your EC2 instance, residing behind a NAT gateway, sends a 1 GB file to Amazon S3, the data transfer cost from the EC2 instance to S3 is free if the transfer occurs within the same region. You only pay the data processing cost for the data passing through the NAT gateway.
To better understand the charges, lets consider an example. Assume a NAT gateway is active for the entire month (730 hours). The hourly charge for the NAT gateway is $0.045. So, the hourly cost will be 730 hours $0.045 = $32.85. Now, imagine your EC2 instances process a total of 100 GB of data through this NAT gateway, and the data processing cost is $0.045 per GB. This data processing cost is 100GB $0.045/GB = $4.50. The total cost for this NAT gateway is $32.85 + $4.50 = $37.35 for the month. These costs are the bare minimum. However, the expenses can climb higher based on the data transfer charges.
Data processing charges apply for each gigabyte processed through the NAT gateway, irrespective of the traffic's origin or destination. Therefore, whether the traffic is coming from your EC2 instance or going out to the internet, the charge is applied, which adds up over time, making it crucial to manage data transfer efficiently.
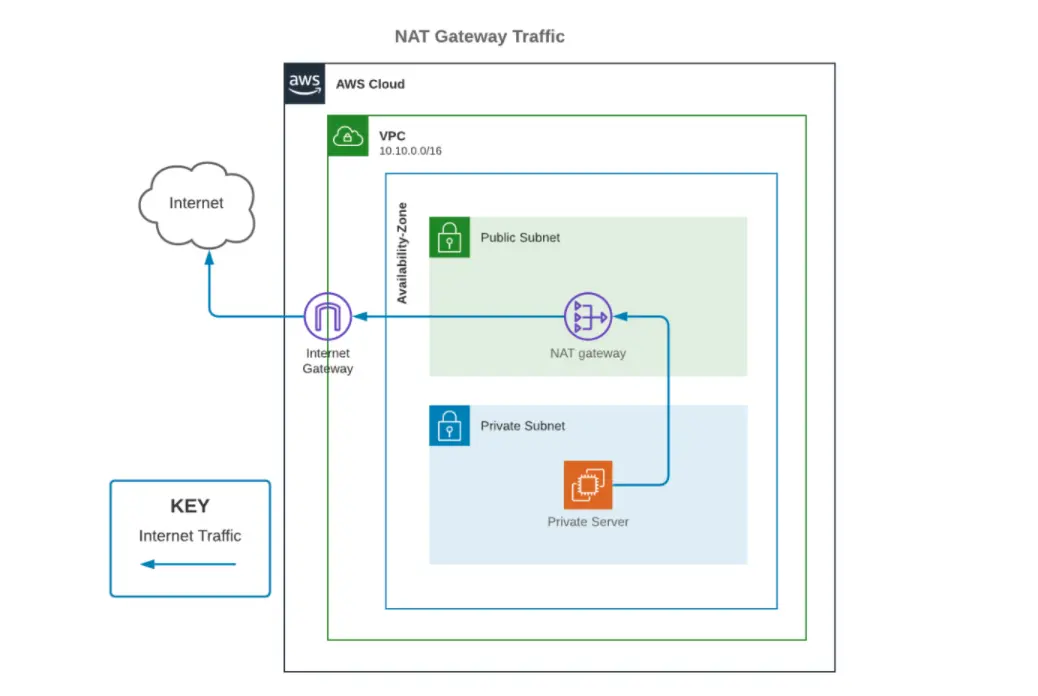
To mitigate the potentially high data transfer costs, several strategic approaches can be implemented. One key strategy is to ensure that your AWS resources that send or receive significant traffic are located within the same Availability Zone as the NAT gateway. When resources reside in the same Availability Zone, this approach minimizes the cross-Availability Zone data transfer costs, which could significantly reduce your overall expenses. This is particularly relevant if your workloads involve large data transfers between AWS resources and the public internet.
Another strategy for cost reduction involves using VPC endpoints for services like Amazon S3, which allows your instances to access these services without needing to traverse the internet. This approach can significantly reduce the volume of data that passes through your NAT gateway and, as a result, reduces the incurred data processing and data transfer charges. This is especially useful for applications that require frequent interaction with S3 for data storage or retrieval. Its a good alternative to using NAT gateways, especially if your resources primarily interact with AWS services.
For a more in-depth cost assessment, use the AWS Pricing Calculator. The calculator helps you explore AWS services and creates an estimate for your use cases. It gives you a clear picture of the total cost.
For resources that communicate frequently with external services, it's also worthwhile to evaluate the volume and the frequency of such traffic. Identify opportunities to cache data locally or to optimize the data transferred. Caching can reduce the number of requests that pass through the NAT gateway, thereby lessening the data processing charges. Optimizing the data volume itself also reduces costs. Techniques like data compression or data summarization can reduce the amount of data that needs to be transferred through the NAT gateway, and also saves on data transfer costs.
Another consideration is the utilization of NAT instances as an alternative to NAT gateways. Although AWS provides NAT gateways as a managed service, NAT instances can offer more cost-effective solutions, particularly if you have highly specific requirements or smaller workloads. For smaller-scale applications, using NAT instances can be a cost-effective measure, reducing the overall impact on your AWS bill.
The cost of a NAT gateway consists of two main components: hourly usage and data processing. The hourly cost is relatively straightforward you pay for the gateway to be available. The data processing cost, however, can be a bit confusing, especially when you aren't seeing any significant outbound traffic. Even if all your traffic is internal, within the same region and Availability Zone, you may still see processing costs. The logic behind this lies in the fundamental operational nature of the NAT gateway, which handles every byte of traffic that flows through it.
Understanding how NAT gateways are implemented is crucial for efficient cost management. NAT gateways are designed with redundancy within a single Availability Zone (AZ). You cannot spin up a single NAT gateway to span multiple AZs. Each AZ needs its own gateway. If your AWS resources transmit or receive a large amount of traffic across different AZs, ensuring that the resources are located in the same AZ as the NAT gateway is essential to minimize costs. Consider creating one NAT gateway in each AZ that contains resources.
Consider the following case study: A company, "CloudCorp," uses a VPC with multiple subnets across three availability zones (AZs). Each subnet requires internet access for its EC2 instances. Initially, CloudCorp used a single NAT gateway in one AZ. The cost breakdown for a month showed hourly gateway charges, plus data processing charges based on the total outbound traffic. However, CloudCorp saw an increase in data transfer costs, especially when traffic between the EC2 instances and the internet was routed. After analyzing their traffic patterns, CloudCorp realized that most outbound traffic originated from the EC2 instances in different AZs than the NAT gateway. This traffic crossed AZ boundaries, leading to higher data transfer costs. CloudCorp then decided to deploy a NAT gateway in each AZ, aligned with the principle of having resources and the NAT gateway within the same zone. They also used VPC endpoints for S3 access, further reducing data transfer through NAT gateways. This strategic move resulted in a significant decrease in data transfer costs.
In summary, minimizing NAT gateway costs requires careful planning and regular monitoring. Keep track of data transfer, use VPC endpoints to avoid using the internet for AWS services, and ensure your resources and NAT gateways are in the same Availability Zone. While it may seem complex, understanding these nuances allows you to make the most of your AWS resources, ensuring cost efficiency while maintaining performance.
If you no longer require a NAT gateway, deleting it via the AWS Management Console, the Command Line Interface (CLI), or the API can prevent further charges. Regularly auditing and optimizing your infrastructure is the best practice for maintaining financial health in the cloud.
Here is a detailed look at the pricing, usage, and optimization of NAT gateways, providing a comprehensive guide to ensure cost-effective cloud architecture.
Article Recommendations
- Juggalo Face Paint Dive Into Its Vibrant Culture And Meanings
- Best Guide For Neti Pot Shoppers Tips And Insights For Optimal Results

Detail Author:
- Name : Louisa Moen
- Username : klockman
- Email : reina15@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1996-08-27
- Address : 2637 Harrison Mountains Flatleyville, TX 16647
- Phone : 920.619.4925
- Company : Rodriguez, Bradtke and Kuphal
- Job : Mail Clerk
- Bio : Ut et perferendis nostrum quis corrupti dolorem reiciendis ex. Quia alias officiis sint aperiam laboriosam vel magni. Dicta voluptatibus repellat qui voluptate voluptatem omnis.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/jammie2752
- username : jammie2752
- bio : Alias libero voluptas rerum accusamus iusto quis. Et a iusto maxime reiciendis ipsa architecto. Natus vero dignissimos molestiae.
- followers : 831
- following : 82
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@leuschkej
- username : leuschkej
- bio : Unde et dolores itaque corporis. Quaerat porro mollitia atque totam iure.
- followers : 6606
- following : 1377
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/jammie3539
- username : jammie3539
- bio : Explicabo minus sequi non laboriosam ut. Vel esse illo sit numquam ea. A est laborum libero.
- followers : 4001
- following : 1537